Corporate bond issuance hits six-month low in September
Despite the slowdown in September, cumulative issuance for the first nine months reached nearly VNĐ398 trillion ($15.1 billion), up 27 per cent year-on-year.
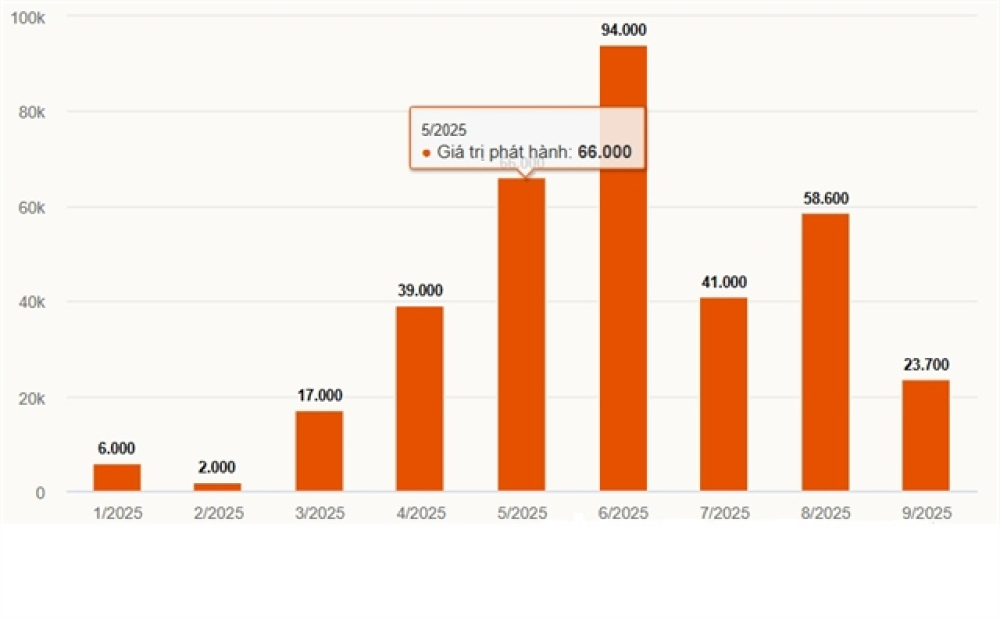
HÀ NỘI — Vietnamese companies issued VNĐ23.7 trillion (US$901 million) in bonds in September, a 61 per cent drop from August and the lowest level in six months, according to the Vietnam Bond Market Association (VBMA).
The market recorded 27 successful offerings last month, down from 43 in August. The figure also represents a 58 per cent decline compared to September 2024.
Despite the slowdown, cumulative issuance for the first nine months reached nearly VNĐ398 trillion ($15.1 billion), up 27 per cent year-on-year.
Banks dominated the market, accounting for 73 per cent of total issuance, followed by real estate firms at 18 per cent.
MBBank led banking sector fundraising with VNĐ6 trillion in September. Most bank bonds have maturities exceeding three years, with some BIDV and TPBank bonds extending 10-15 years as lenders seek medium- and long-term funding.
The real estate sector cooled significantly after months of accelerated issuance for debt refinancing. Only three property developers issued bonds in September, totalling less than VNĐ1.5 trillion, with interest rates ranging from 9.2 to 10.5 per cent annually.
Early redemptions also declined 8 per cent year-on-year to VNĐ19.5 trillion. Five bond codes experienced delayed principal or interest payments, worth approximately VNĐ150 billion.
VBMA estimates VNĐ48 trillion in bonds will mature in the final quarter, with real estate accounting for 38 per cent or over VNĐ18.3 trillion. Maturity pressure peaks in December at VNĐ33 trillion.
Meanwhile, secondary market trading improved 45 per cent, averaging VNĐ7.5 trillion per session, indicating sustained investor interest despite lower new issuance.
Major companies including Vingroup and Vietjet have announced plans to return to the bond market this year, with proposed issuances of VNĐ2.5 trillion and VNĐ3 trillion respectively.
Mirae Asset Securities Vietnam’s analysts note that the bond default rate has stabilised at 12.4 per cent, though many property developers still struggle with cash flow to meet bond obligations.
The recovery outlook remains mixed, however. While financially strong developers like Vinhomes continue accessing bond markets and attract foreign capital through M&A deals, weaker firms relying on maturity extensions face challenges due to limited credit access and insufficient credit ratings.
Source: VNS
Photo: vneconomy.vn





